Charting the way towards the future: how the modeling with system dynamics can address the demographic challenge. The case of SPANDAM.

The dynamic systems it is a methodology that is used to study complex situations through simulation models. This methodology, which is applied in different fields such as physics, chemistry or economics, among others, it is being used in the phase of project modeling SPANDAM to study and predict actions in regions at risk of depopulation.
In the article today, David Vegas Merino and Juan José Mediavilla, of the University of Valladolid, we have the variables that were taken into account in this phase of work with the prototype of the model that is going to be Spandam.
DYNAMIC SYSTEMS
The dynamics of systems is a work methodology based on the development of simulation models for the study of complex situations under a set of given conditions. The general purpose of these models focuses on the study of the behavior of certain variables over time.
It is worth noting the flexibility and diversity in terms of the fields of application of this methodology, some of the experimental physical chemistry, predictions of behavior in economic systems or the study of regions at risk of depopulation, as is the case of SPANDAM.
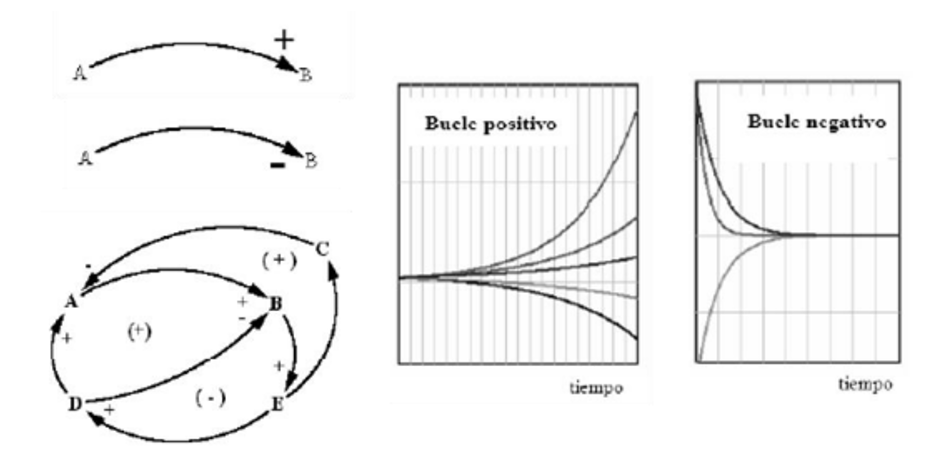
This methodology of work has as a basis the relationship between variables, whether in a positive way (variables A-B) or negative (variables (C-D). Greater, in those cases in which the combination of these relationships to close over the variable start is giving rise to feedback loops. These loops serve to a classification key in reinforcing or stabilizers, depending on whether diverge or converge over time toward a value.
MODELING
Relative to the model itself SPANDAM this structure consists of 10 modules, being key to the multiple relationships between them. So, we have the module demographic, which is the main, economic, educational, health, housing, transport and communications, cultural, environmental, and social services values and social capital. The way in which they interrelate can be summarized in the following graph.
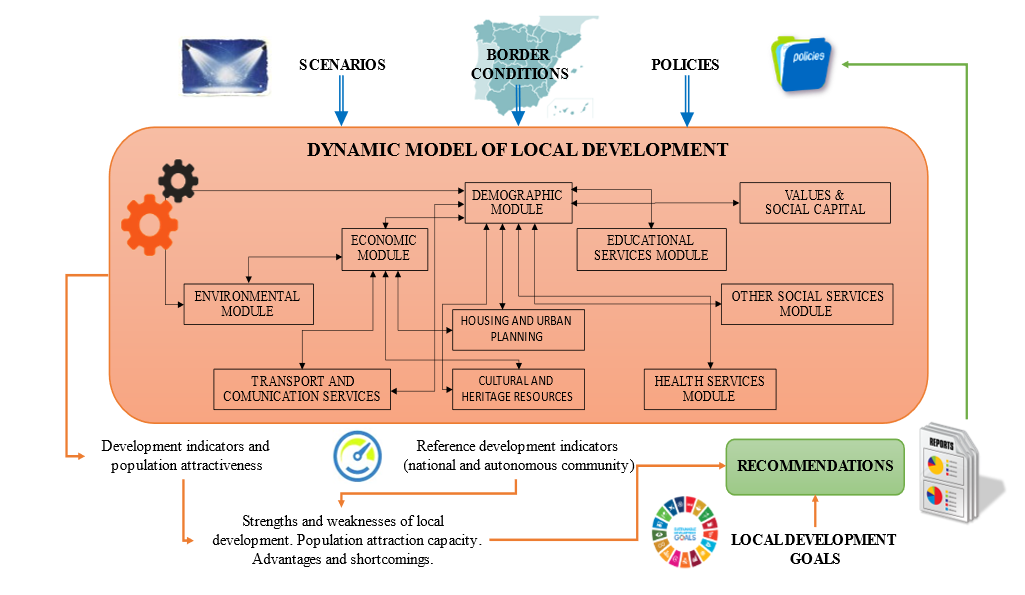
Then, as an example, we describe the central module of the model: the module demographic. It has a capital importance for the whole of the model to be migratory dynamics the main objective to study. On the other hand, to be sued the population by various modules for its correct operation. Examples of this is the need of the population for the calculation of students in the educational module or the active population in the module economic.
Initially, it was deemed necessary to segment the population in 101 age groups (C0, C1, ..., C99, C100+), which in turn differentiated according to sex. In this way, the module demographic contemplates 202-groups of the population. Each of these segments are treated as stocks, according to the Dynamics of Systems; they are filled by the population of the previous stock and immigration, is flushed by deaths, emigrations and the aging population that goes to the next stock.
Births, deaths and births are calculated in a manner proportional to the population through their respective rates. On the other hand, the immigrations are calculated endogenously through the index of attractive population, which comprise different indicators calculated in the model are classified in 7 dimensions
CONCLUSIONS
The simulation model SPANDAM allows you to make projections in specific scenarios of regions at risk of depopulation. In this way, the final tool will have a governmental level, it will try to give suggestions to public agencies; and a user level, in which the end-user will be able to evaluate that policy measures have a greater impact in accordance with the objective.
